Cannabidiol (CBD)
Cannabidiol (CBD) has a rich and evolving history that traces back to its initial discovery in the mid-20th century. The compound was first isolated in 1940 by Roger Adams, a pioneering chemist at the University of Illinois. Although Adams successfully extracted CBD from the cannabis plant, the compound’s precise structure and the full range of its properties were not yet known. This early discovery laid the groundwork for future research.
The 1960s were a pivotal period for cannabinoid research, largely due to the work of Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, an Israeli chemist often referred to as the “father of cannabis research.” In 1963, Mechoulam and his colleagues successfully identified and mapped the chemical structure of CBD, differentiating it from its psychoactive counterpart, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which he described a year later in 1964. This landmark achievement allowed scientists to better understand how CBD and other cannabinoids interact with the human body.
In the 1970s, the focus shifted toward exploring the potential medicinal applications of CBD. Early studies suggested CBD’s efficacy in reducing symptoms such as nausea and anxiety. The 1980s brought significant research advancements, particularly in the realm of epilepsy. Dr. Mechoulam conducted a 1980 study that indicated CBD could reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in patients, sparking broader interest in its therapeutic applications.
The story of Charlotte Figi in the 2010s played a crucial role in popularizing CBD and reshaping public perception. Charlotte, a young girl with Dravet syndrome, experienced up to 300 grand mal seizures a week. After conventional treatments failed, her parents turned to CBD oil derived from a strain of cannabis known as Charlotte’s Web, named in her honor. The results were groundbreaking, reducing her seizures to only a few per month and bringing global attention to CBD as a potential treatment for severe forms of epilepsy.
This growing interest and mounting anecdotal evidence spurred significant changes in policy and public attitudes. In 2018, the U.S. Farm Bill was signed into law, legalizing the cultivation and sale of industrial hemp and removing hemp-derived CBD from the list of controlled substances. This legislation opened the door for further research, commercial growth, and widespread availability of CBD products.

Pharmacokinetics
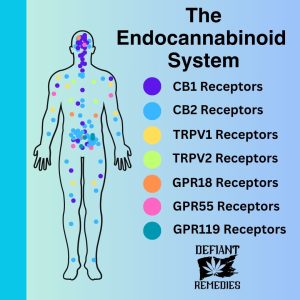
While the full complexity of how CBD impacts the endocannabinoid system is not understood, numerous scientific studies have demonstrated CBD’s effect on the mind and body. CBD interacts with a very wide range of receptors, which explains its broad effects. CBD interacts with the CB1 and CB2 receptors, but it only has a weak affinity for them. CBD can act as an antagonist for both receptors. CBD does have a greater affinity for CB2 receptors than CB1 receptors. However, much of CBD’s therapeutic effects stem from its ability to suppress the enzyme that breaks down anandamide, thus keeping anandamide active at higher concentrations and for longer duration.
CBD interacts with the G-protein receptors GPR18 and 55, and the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. CBD seems to inhibit and modulate a wide range of receptors and ion channels throughout the body.
GW Pharmaceuticals
CBD was unknowingly being bred out of cannabis until 1998, when GW pharmaceuticals began searching for high CBD strains. GW was co-founded in 1998 by Dr. Geoffrey Guy and Dr. Brian Whittle in Great Britain, where they secured licenses to grow cannabis for research purposes.
GW pharmaceuticals, which was purchased by Jazz Pharmaceuticals, began marketing the anti-seizure drug, Epidiolex, and the MS drug, Sativex, both of which have CBD as an active ingredient.
EPIDIOLEX is the first and only FDA-approved prescription CBD used to treat seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS), Dravet syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) in patients 1 year of age and older. Epidiolex Sativex contains both THC and CBD in equal parts. It is an oromucosal spray approved in many European countries for treating spasticity. It is an investigational drug in the United States.

